Renovascular Disease
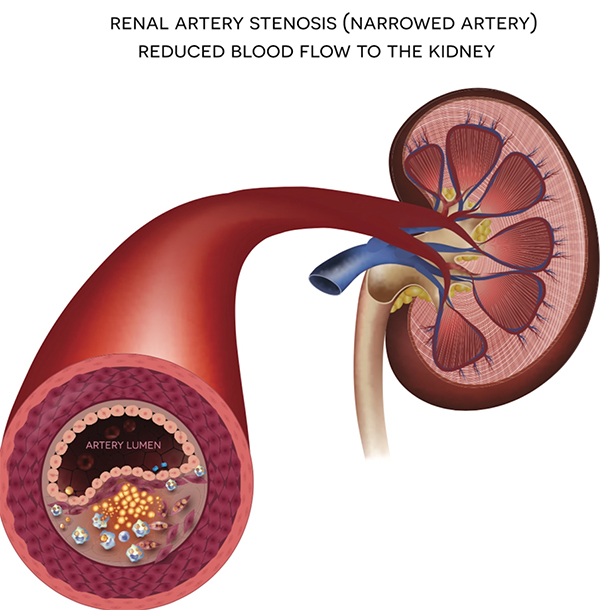
The kidneys filter blood and remove waste from your body in the form of urine, which collects in your bladder and exits your body when you urinate. The kidneys also help to control your blood pressure (BP) by secreting a hormone called renin into your bloodstream. The renal arteries supply fresh blood and renal veins drain used blood from the kidneys..
Renal artery stenosis is a condition characterised by narrowing of the kidney arteries, which is caused due to the accumulation of cholesterol and calcium plaque on the walls of the artery. Obesity, smoking, high cholesterol levels and diabetes are some of the risk factors that increase your chances of renovascular disease. Renal vein thrombosis is where the renal vein is blocked partially or completely by blood clot and this can happen in nephrotic syndrome (high levels of albumin protein excreted through urine), in the presence of a tumour, infection or injury to the vein and also when clots formed elsewhere travel towards the renal vein and get stuck.
Renovascular conditions progress slowly over time and may not cause noticeable symptoms initially. Symptoms may include elevated blood pressure, decreased kidney function and a bruit (whooshing sound in the abdomen) heard with a stethoscope. Renal vein thrombosis can also affect the kidney function but more importantly the clot can also extend to or travel with the flow of blood into healthy blood vessels and block the flow of blood from other vital organs. In the lungs, it can cause a serious life threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. Symptoms related to this may be pain in the abdomen and back, , protein or blood in urine, fever, vomiting, nausea and difficulty in breathing.
How is Renovascular disease investigated
When you present to the clinic with any of these symptoms, your doctor may suggest the following imaging tests to help determine renovascular disease:
- Ultrasound: uses sound waves for imaging blood vessels
- CT scan: cross-sectional images of the blood vessels are obtained using Xray.
- MRA scan: uses magnetic fields to image blood vessels
- Radionuclide scanning: uses radioactive chemicals for imaging
- Angiography: employs the use of Xray to detect contrast ( a special dye) in the blood vessels.
- Venacavography: a form of angiography that takes images of the main abdominal veins
Treatment Options
Based on the severity of your condition, your physician may recommend the following treatment options:
You can prevent or reduce risk of renovascular diseases