Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
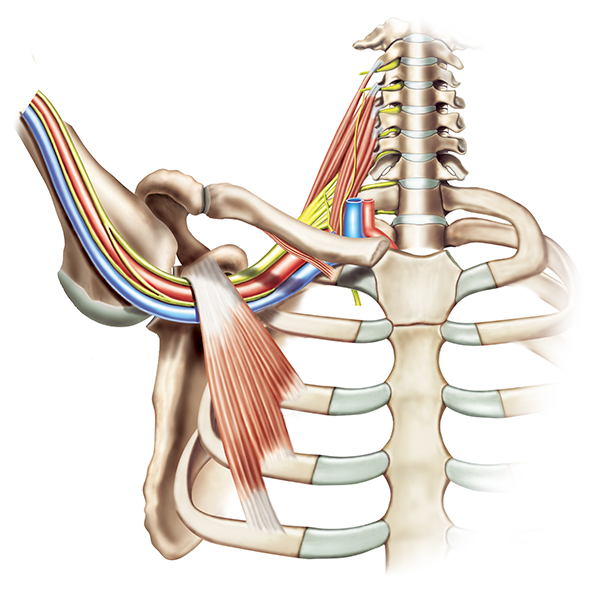 Figure illustrates the confined space in the thoracic outlet
Figure illustrates the confined space in the thoracic outletThe thoracic outlet is a narrow passageway leading from the base of the neck to the armpit and arm. This passageway contains blood vessels, nerves and muscle. When this passageway becomes compressed the condition is termed as thoracic outlet syndrome. This rare condition is predominantly characterised by burning pain in the neck and shoulder, numbness and tingling of the fingers and weak hand grip. Thoracic outlet syndrome generally occurs within the age group of 20 to 60 years and is more common in females than in males. There are 3 types of thoracic outlet syndrome depending on which component is compressed, namely neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome, arterial thoracic outlet syndrome and venous thoracic outlet syndrome
What are the causes of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome?
Thoracic outlet syndrome can result due to injury, tumours that press nerves, poor posture that compresses nerves, weight lifting, anatomical defects such as an elongated C7 transverse process and cervical ribs, anomalous tissue overgrowth, upper thoracic neurovascular compression, costocoracoid tendon, subclavian muscle hypertrophy and so on.
Symptoms
The symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome may include numbness and pain in the neck, shoulder and arm, tingling or burning sensation, weakness, limited range of movement of arms, and swelling or redness of your arm, or colour changes to the arm or hand.
Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis is very essential for the condition of thoracic outlet syndrome. To evaluate your condition, your doctor will perform a physical examination and collect your medical history. You may be advised to have a chest X-ray, MRI or CT scan. Nerve conduction velocity study may be suggested to check the conduction of electrical signals in the nerves.
Treatment
The treatment of thoracic outlet syndrome involves both non-surgical and surgical approach.
Nonsurgical Treatment
-

Physical Therapy
- Physical therapy- Exercises can decrease the pressure on the nerves and blood vessels and also strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder. Maintaining proper posture can help you stand, sit and walk straight.
-

Medications
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications- can reduce the pain and swelling.
-

Lifestyle Changes
- Weight loss- reducing your weight, if you are considered over weight.
- Lifestyle changes- avoid strenuous activities and other activities that increase the risk or symptoms.
Surgical Treatment
-

Surgery
- If nonsurgical treatment does not alleviate your symptoms, your doctor may advise surgery. Surgery may involve removing a portion of an abnormal first rib or releasing a muscle that joins the neck and chest. The surgery will depend on the cause of the compression.
